Copyright 2014
Principles
Physiology relates to the interaction of the forces in the body. The forces have both physical and chemical forms.
Genetic Forces
 |
Power of the Genes
71586b08.800 brain parts masks pink anatomy genetics genes generations coronal projections MRI Davidoff art Davidoff MD
Forces in the Central Nervous System
Chemical Forces Allowing Impulse Transmission Across a Synapse
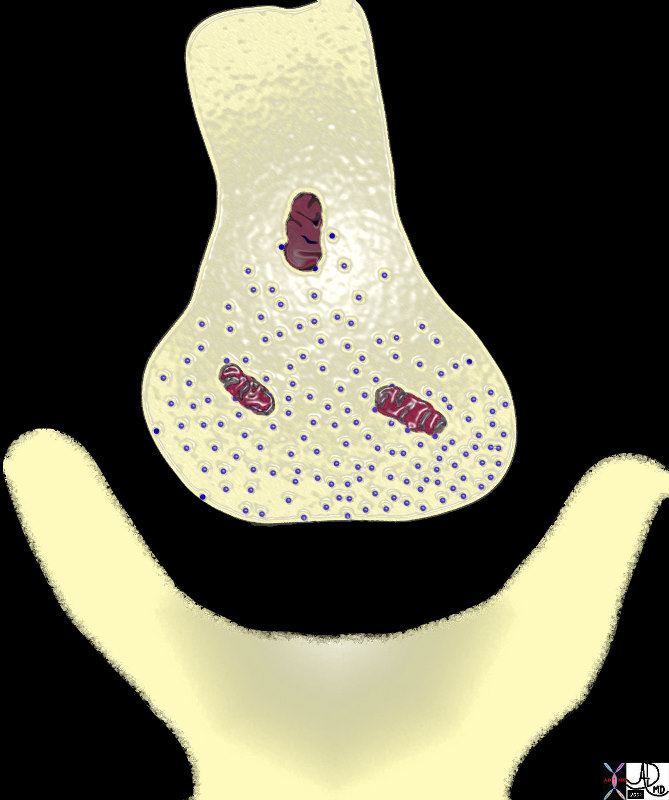 |
Synaptic Cleft Requiring Chemical Transmitters eg Acetylcholine to Transmit Impulse Across Nerve Junctions
72046.800 mitochondria transmitter vesicles presynaptic terminal post synaptic terminal soma of neuron synaptic cleft acetyl choline norepinephrine dopamine serotonin forces chemical energy function principles Davidoff art Davidoff drawing Davidoff MD
Electrical Transmission Along a Nerve
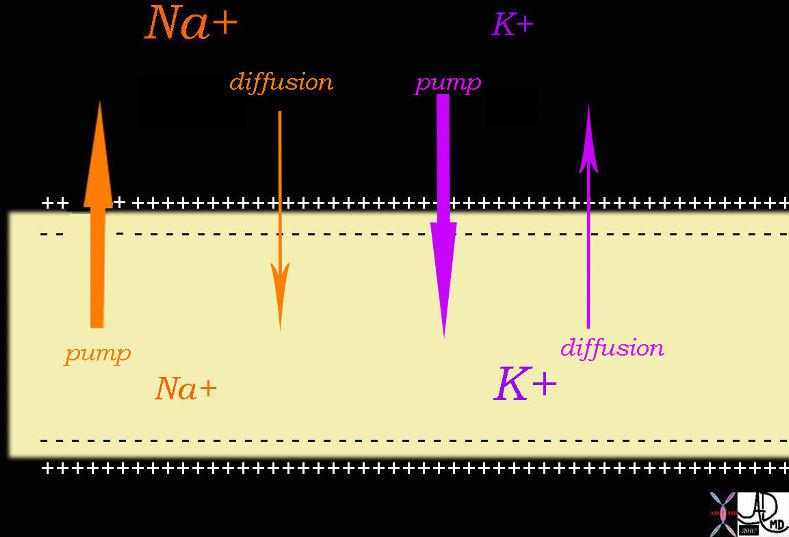 |
Sodium Potassium Pump MEchanism in the Transmission of a Nerve Impulse
72045b04.800 nerve conduction force electricity electric force positive force negative force sodium pump Na pump Patassium pump K+ pump diffusion conduction of impulses Davidoff drawing Davidoff art Davidoff MD
Forces in the Cardiovascular System
Creating Pressure Gradients
 |
Creating Pressure Gradients by Muscular Pump Action49483b01 heart cardiac LV left ventricle aorta aortic systemic circulation capillary capillaries arterioles venules right atrium RA right ventricle RV normal physiology pressures hemodynamics Davidoff MD Davidoff art
Mechanical and Electrical Forces
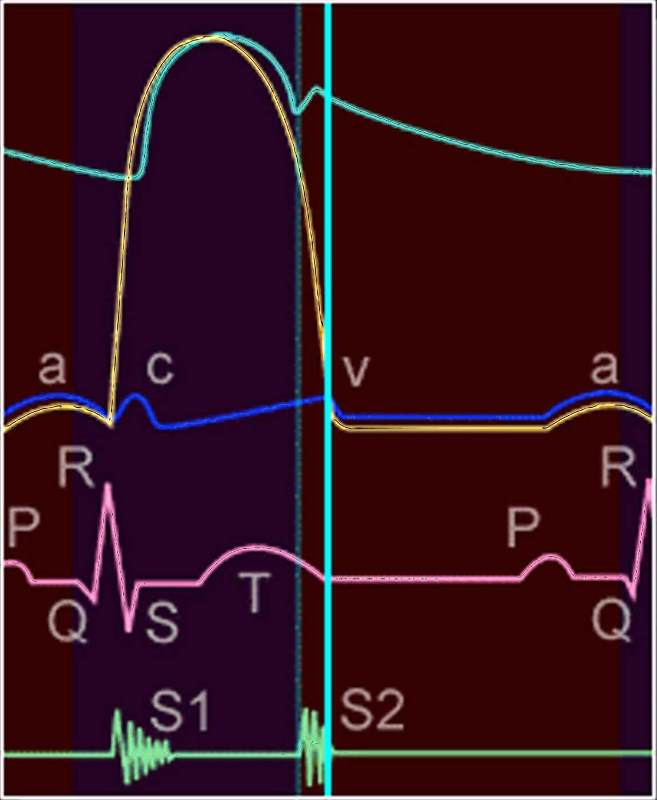 |
Wiggers Diagram – Pressures in th Cardiovascular System33808b.800 heart cardiac physiology pressure EKG ECG pressure curves diagram LV aorta LA left atrium left ventricle systole diastole acv waves Davidoff MD
Elastic Forces
 |
Elastic Forces
This CTscan shows a theoretical changes of the aortic wall during diastole (a) sytolic expansion (b) and return to normal in diastole (c) In systole (b) the suprarenal artery is expanded by the pulse but is relatively decompressed by the the low resistance and high flow renal arteries. The infrarenal aorta is relatively more expanded in systole (b) since the iliac arteries offer a relative resistance. This increased resistance causes the elastic tissue in the aorta to stretch (b) so that the recoil in diastole (c) results in a sustained forward moving force assisting the blood to get to their most distal destination – the feet. When the aorta starts to lose its elasticiy the recoil of systole gradually is weakened so that the aorta does not return to its normal diameter after each systolic expansion. Over many years this lack of recoil is progressive so that the resulting wall is weaker and dilated, until an aneurysm can be formed.
Courtesy Ashley Davidoff 24877c03 code CVS artery aorta AAA infrarenal circulatory elasticity recoil
 |
Fluid Gradients at the Capillary Level
42445b03d06 capillary interstitium arteriole arteriolar pressure capillary pressure venule venular presure interstitial pressure colloid osmotic pressure plasma colloid osmotic pressure Forces tending to move fluid out of the capillary is capillary pressure of 25mmHg, negative intertitial presure = 6mmHg and and interstitial osmotic pressure of 5 mmHg = total of 36mmHg Forces holding the holding the fluid in the capilaries include the plasma oncotic pressure of 28mmhg and thus the net outward force is about 8mmHg Davidoff art Davidoff drawing Davidoff MD
Respiratory System
Moving Forces
 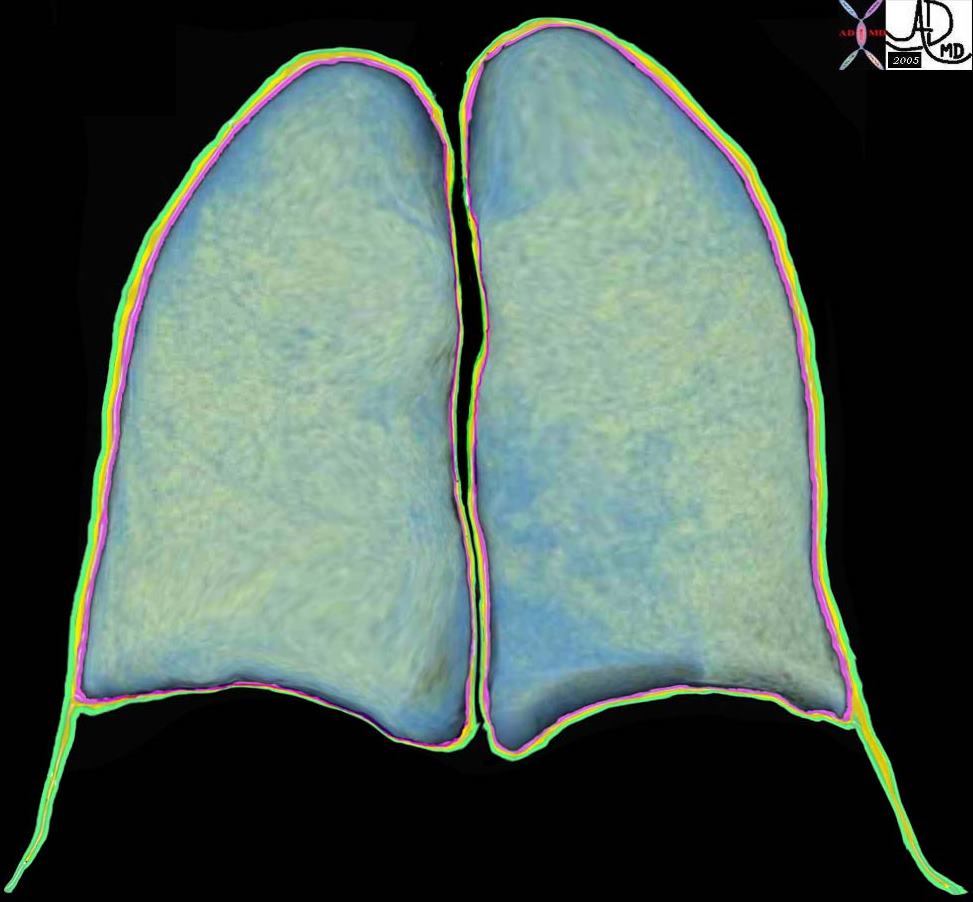 |
Keeping the Lungs attached to the Chest Wall via A Two Layered Pleura – Capillary Forces
The coronally reformatted image of the lung parenchyma has been outlined with the visceral pleura, (pink) the pleural fluid in the pleural space, (orange) and the parietal pleura. (green) Note how at end expiration the parietal pleura in the costophrenic sulcus extends beyond the lung margin so that the visceral pleura is absent in the costophrenic sulcus and there are two layers of parietal pleura facing each other. During inspiration the lung expands into this space. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 32634b10 lung pleura pulmonary
32634b10
45771 chest lungs fx normal chest CT anatomy Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Davidoff art 45769 45770 45771 45772 45773 45774 45775 45776
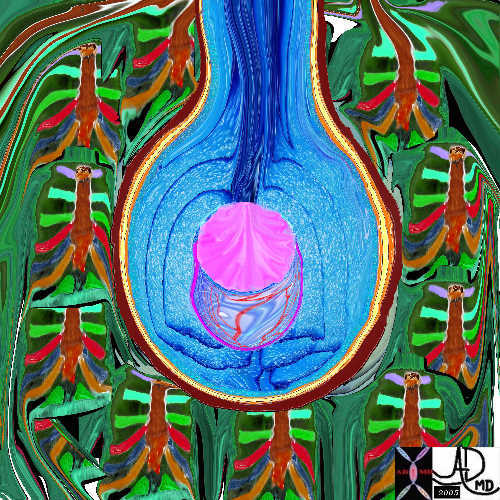 |
Mechanical Forces Bringing Air to Alveoli
Chest Wall, Diaphragm, Alveolar Expansion
The five major layers that keep the air moving include the outer bony cage, the muscular layer represented in maroon, the pleural complex (orange yellow orange) the lung (blue) and surfactant within the alveolus. (pink) Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD. 42530b05b09b01a08 Davidoff art
Gradients Createrd at the Alveolar Level
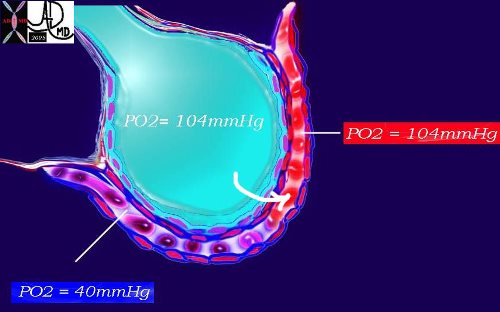 |
Oxygen Gradients Created by the Lungs Across the Alveolar Membrane
This diagram again shows the alveolus in teal, the arteriolar component of the capillary with red cells in blue and venular component replenished by oxygen in red. As noted above, the PO2 of the arterial blood is 40mmHg while the inspired air is 104mmHg. A pressure gradient thus exists and diffusion from the high to the low pressure occurs with a net movement of oxygen into the blood to equilibrate the pressure. Venous blood is now rich in oxygen with a PO2 of 104mmHg.
Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD. 42445b08b Davidoff art
Chemical Forces Used to Maintain Patency of Alveoli
 |
Chemical Force of Surfactant to Keep the Alveoli Open during Respiration
This a grape like cluster of normal alveoli. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 32163 code lung alveolus terminal bronchiole respiratory bronchiole RS normal anatomy drawing Davidoff art
Gastrointestinal System
Chemical Forces – Acid Production by the Stomach for Antimicrobial Action
 |
PH probe to Detect Gastric Acid Reflux During Surgery49462 chest esophagus PH probe intraoperative monitoring for aspiration of stomach contents CXR plain X-Ray of the chest Davidoff MD
Forces for the Processing of Food
 |
Chewing Carbohydrates with Chemical Action of Amylase results in Glucose Availability
62306b05p.800 food carbohydrates dessert almonds nuts blueberry blueberries chocolate chewing mastication amylase chemical forces breakdown enzyme catabolism glucose Davidoff art Davidpff photography Davidoff MD
 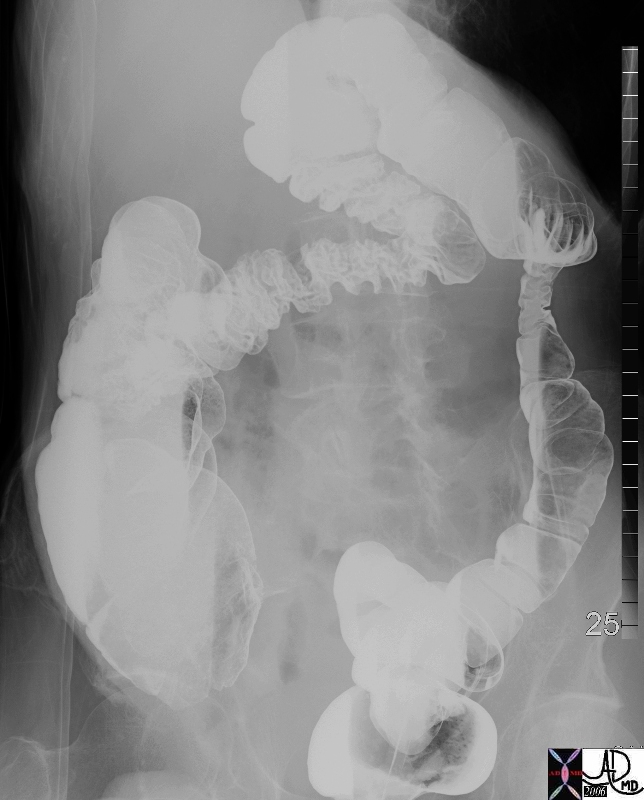 |
Pump Action – Peristalsis Moving it On for Further Processing
39548b03 stomach antrum fx narrowing with normal mucosal folds dx antral contraction wave antral peristalsis normal UGI uper GI barium imaging radiology
45660 elderly male colon large bowel cecum ascending descending colon sigmoid colon hepatic flexure splenic flexure fx peristalsis fx normal anatomy and physiology BE barium enema Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 45660 45661
Genitourinary Tract
Pressure Gradients and Osmotic Gradients
 |
The Initial Filter – Bowman’s Capsule – and then
Countercurrent Mechanism in the Tubes of Henle to Generate a Gradient to Recapture
Water and Excrete and Secrete Uriniferous Waste
16100b.800 kidney renal arteriole Bowman’s capsule filter tubule proximal convoluted tubule distal convoluted tubule collecting tubule ureter countercurrent mechanisms urine production gradients membrane flter bladder urethra drawing Davidoff art Davidoff MD
 |
Peristalsis in Ureter and Bladder – Contraction to Move Urinary Waste Out
31843 kidney ureters bladder post void calyces pelvis post void forces physiology contraction IVP physiology Plain X-ray KUB Davidoff MD
Muscular Forces
 |
Contracted Fetal Biceps
47757b02 24 week fetus arm hand biceps thumb index finger human opposing thumb and index grape in hand normasl anatomy MRI Davidoff MD concepts Davidoff food in the body
 |
Coordinated Muscular Forces80753pb01.800 Dancers Arielle Davidoff art Davidoff photography Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
 |
Running64163b01 health youth age time physiology boy running happy davidoff photgraphy Davidoff MD
Skeletal System
 |
Design of the Joints Disc Material and Shape of the Spine to Accomodate the MEchanical and Gravitational Forces Created with the Evolution of the Upright Position
47717c01 bone spine lumbar spine scotty dog pedicles normal obliques Davidoff animals in the body plain film X-ray Davidoff MD
 |
Gravitational and Muscular Forces result in Moulding of Bone to Accomodate the Mechanical Forces
49464 bone femur fx healed fracture compensation total knee replacement plain X-Ray Davidoff MD 49465